Data Consistency vs Data Integrity: Similarities and Differences
Databand.ai
AUGUST 30, 2023
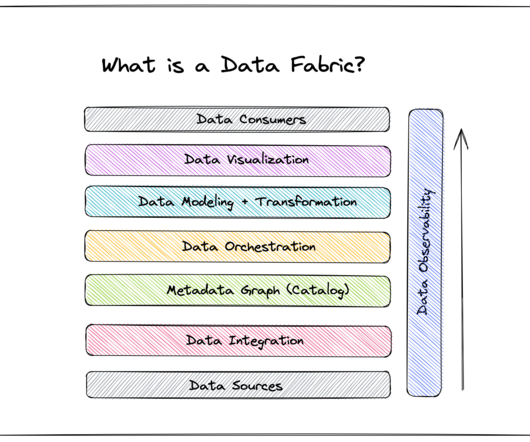
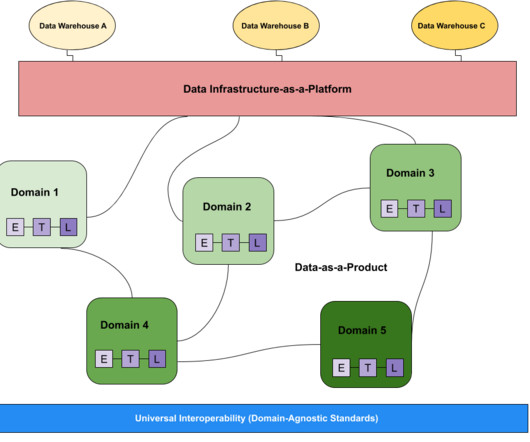
It plays a critical role in ensuring that users of the data can trust the information they are accessing. There are several ways to ensure data consistency, including implementing data validation rules, using data standardization techniques, and employing data synchronization processes.








































Let's personalize your content