Data Integrity vs. Data Validity: Key Differences with a Zoo Analogy
Monte Carlo
MARCH 24, 2023
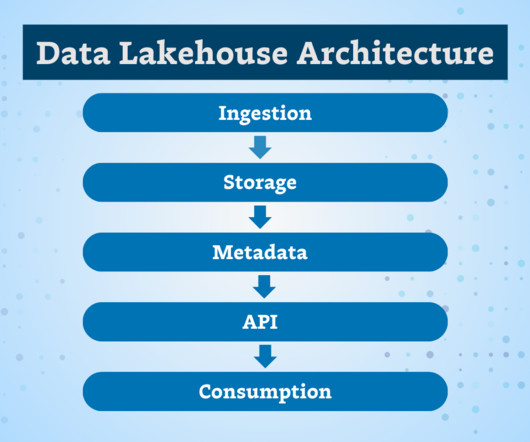
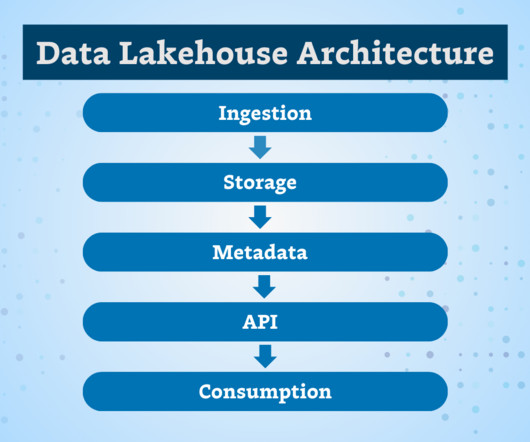
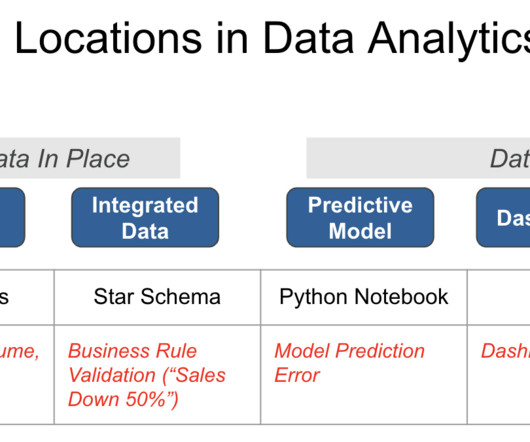
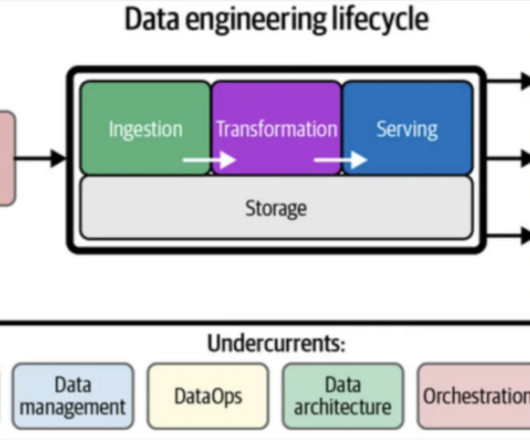
The key differences are that data integrity refers to having complete and consistent data, while data validity refers to correctness and real-world meaning – validity requires integrity but integrity alone does not guarantee validity. What is Data Integrity? What Is Data Validity?










Let's personalize your content