RDBMS vs NoSQL: Key Differences and Similarities
Knowledge Hut
MARCH 15, 2024
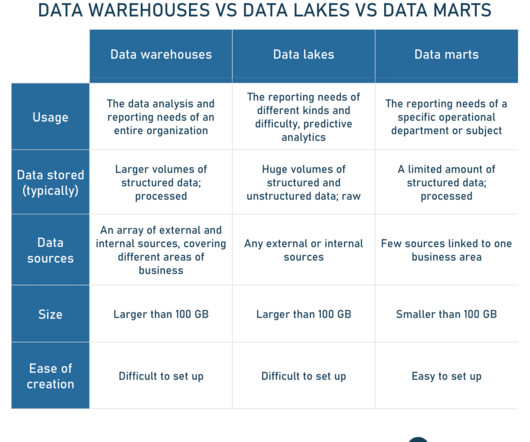
Making decisions in the database space requires deciding between RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) and NoSQL, each of which has unique features. RDBMS uses SQL to organize data into structured tables, whereas NoSQL is more flexible and can handle a wider range of data types because of its dynamic schemas.











Let's personalize your content