Data Collection for Machine Learning: Steps, Methods, and Best Practices
AltexSoft
JUNE 26, 2023
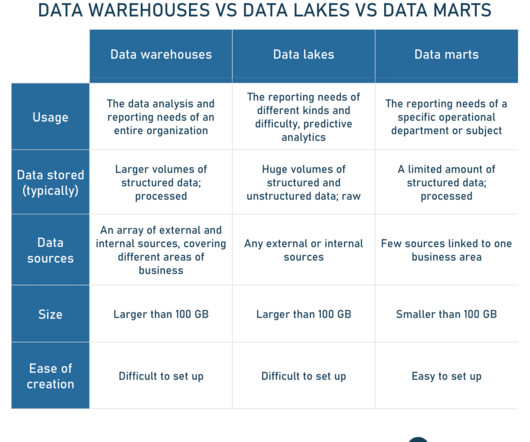
The ultimate goal of data integration is to gather all valuable information in one place, ensuring its integrity , quality, accessibility throughout the company, and readiness for BI, statistical data analysis, or machine learning. Key differences between structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.




Let's personalize your content