AWS vs Azure-Who is the big winner in the cloud war?
AWS vs Azure -A key comparison of the leading public cloud service providers that will help you understand which cloud is best for business use case .

This blog compares the topmost leaders of the cloud computing industry—Amazon and Azure—which account for more than 50% of the market share. Both platforms will be compared on various parameters such as pricing, database features, networking connectivity, machine learning tools, etc.
AWS Project-Website Monitoring using AWS Lambda and Aurora
Downloadable solution code | Explanatory videos | Tech Support
Start ProjectAWS entered the cloud service market in 2006, initially supporting Amazon's e-commerce. It swiftly evolved into a robust suite of cloud services, becoming a global industry leader. Microsoft recognized the cloud's potential and launched Azure in 2010, leveraging its enterprise ties and software expertise to expand Azure's capabilities rapidly. Azure's market share has grown steadily due to its comprehensive services and seamless integration with Microsoft's products like Windows Server, Office, and Dynamics.
Today, AWS and Azure stand as undisputed leaders in the cloud service market, frequently leaving businesses with a crucial decision: which platform to choose? Azure excels as a powerful Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) provider with superior Windows integration, while AWS offers extensive Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) options and diverse tools. This article will highlight the competition between the two heavyweights of cloud services – Azure vs. AWS. We'll check out an overview of AWS and Azure and consider the critical considerations for choosing Azure or AWS. You can also refer to this article if your organization is unsure about moving from AWS to Azure.
Table of Contents
- Azure vs. AWS - Which cloud is best?
- AWS vs. Azure - Overview
- Azure vs. AWS - Computation power
- Azure Cloud vs. AWS Cloud – Storage
- Azure or AWS - Which is better in terms of Pricing?
- Amazon AWS vs. Microsoft Azure – Databases
- Azure vs AWS–Content Delivery and Networking Connectivity
- Amazon AWS vs. Microsoft Azure - Machine Learning
- Azure Compared to AWS: Job Opportunities
- AWS vs. Microsoft Azure: Salary
- AWS versus Azure: Difficulty Level
- AWS vs. Azure: Market Share for Q1 2024
- Microsoft Azure versus AWS: Certifications
- Microsoft Azure vs. Amazon AWS: Learning By Doing
- Azure or AWS: Who will lead in the future?
- Azure vs. AWS - Which is better?
- FAQs
Azure vs. AWS - Which cloud is best?
If you are in a hurry to learn about the comparison between Azure and AWS, we recommend you skim the table below.
|
AWS |
Azure
|
|
Amazon's on-demand cloud computing service |
Microsoft's public cloud infrastructure |
|
From the start, it has supported the open-source model. |
Connection with the open-source community is strained. |
|
In terms of government cloud products, it has an advantage over Azure. |
Whenever it comes to government cloud services, there is a confined scope. |
|
Adaptable pricing system |
When opposed to AWS, the pricing structure is less adaptable. |
|
AWS is continually improving its Hybrid Cloud solutions. |
Organizations can link local servers with Cloud instances, which benefits in the hybrid cloud space. |
|
AWS has a product marketplace for Windows and Linux with a vast network of partners. |
Azure is indeed growing its digital ecosystem despite the limited Linux alternatives. |
|
For big data, EBS storage is incredibly fast. |
Big data poses challenges for standard storage, demanding premium storage. |
|
For big data, much more advanced cloud infrastructure is required. |
Although Azure's services are less developed for big data, they are improving. |
|
Specific machines can be monitored. |
Cloud services are made up of machines that respond to the same domain name but with distinct ports. |
|
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a pay-per-hour cloud computing service. |
Pay per minute for Azure Infrastructure Services. |
|
S3 — Archiving and retrieval for a short period of time. Amazon Glacier supports long-term data archiving and retrieval. |
Blobs, Queues, and Tables are similar to those found in S3. There is currently no option for long-term data archiving and retrieval. |
|
User-defined roles with unique permission controls are used to provide security. AWS also provides an excellent implementation of granular IAM and security groups. |
Azure Active Directory is a single source for permission management and authorization. Unlike AWS where users, federation, and access to each account has to be configured, Azure lets you do this from a single directory. |
AWS vs. Azure - Overview
AWS and Azure offer the same basic capabilities around flexible computation, storage, networking, and pricing. Both share the common elements of a public cloud – autoscaling, self-service, pay-as-u-go pricing, security, compliance, identity access management features, and instant provisioning. But before we dive into the details and compare them with such features, let us look at a quick overview of the two cloud computing platforms.
AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the most experienced and oldest player in the cloud computing space, with 11 years in operation. It provides a wide range of services (over 200!) to access and manage online applications. Even though AWS is commonly used in various cloud computing projects, it isn't without drawbacks. While it offers unmatched scalability, cost-effectiveness, and a vast range of services, its complexity can be intimidating for beginners in cloud computing. Additionally, the responsibility for proper security configuration falls on the user, and migrating away can be challenging. AWS may be better for cloud engineers who prioritize control over flexibility and are comfortable managing intricate systems. However, for its unmatched range of features, scalability, and proven reliability, AWS remains a top choice for businesses of all sizes.
Azure
Azure is a cloud computing platform by Microsoft. It allows users to access, manage, and develop applications and other services on a cloud rather than a physical server. It is a strong contender in the cloud computing world, boasting high availability, robust security, and a focus on integrating existing Microsoft products. This integration feature makes it a natural fit for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. It also offers a pay-as-you-go model and a wide range of development and data engineering tools. However, Azure can be complex for beginners, and data egress fees (charges for transferring data out of Azure) can add unexpected costs. Azure is, thus, a secure and scalable platform for businesses relying on Microsoft products, but it requires some expertise to navigate effectively.
Let's understand what each cloud provider brings to the public cloud table and the key differences between Microsoft Azure vs. AWS.
Here's what valued users are saying about ProjectPro

Gautam Vermani
Data Consultant at Confidential

Ameeruddin Mohammed
ETL (Abintio) developer at IBM
Not sure what you are looking for?
View All ProjectsAzure vs. AWS - Computation power
AWS' principal computing solution is its EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances, which offer flexible computing on request and can be tailored for various applications. It offers various EC2 instances tailored to multiple workloads, including General Purpose, Compute Optimized, Memory Optimized, Storage Optimized, and Accelerated Computing. In contrast, Azure's compute services are built on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) and include many other tools that help deploy cloud-based applications. Its comprehensive array of Virtual Machines (VMs) includes General Purpose, Compute Optimized, Memory Optimized, Storage Optimized, and GPU categories, ensuring businesses can find the right fit for their needs.
Both platforms excel in scalability. AWS adjusts EC2 instances based on demand and offers Spot Instances for cost-effective use of unused capacity. Similarly, Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets enable automatic scaling to match demand, while Azure Spot VMs provide economical solutions for interruptible workloads.
Serverless computing is another area where both platforms shine. AWS Lambda allows code execution without infrastructure management, while Azure Functions offers a robust, serverless environment for running code seamlessly. For batch processing, AWS Batch makes running batch jobs easier by managing compute resources. For high-performance computing (HPC), AWS provides tools like Elastic Fabric Adapter and AWS ParallelCluster. Similarly, Azure Batch handles job scheduling and scaling, while Azure's HPC services, including InfiniBand networking and CycleCloud, simplify managing HPC environments.
Additionally, AWS's Graviton processors deliver significant cost-performance benefits for specific applications. On the other hand, with its seamless integration into Microsoft's software ecosystem, Azure presents a compelling option for enterprises heavily invested in Microsoft technologies.
|
Service offered |
AWS |
Azure |
|
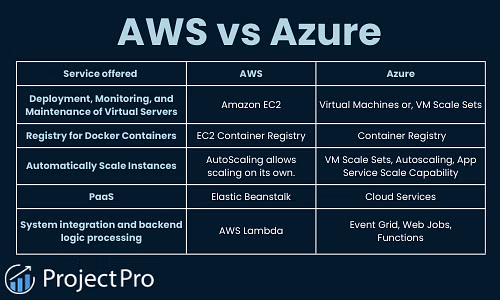
Deployment, Monitoring, and Maintenance of Virtual Servers |
Amazon EC2 |
Virtual Machines or, VM Scale Sets |
|
Registry for Docker Containers |
EC2 Container Registry |
Azure Container Registry |
|
Container Orchestration |
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) |
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) |
|
Automatically Scale Instances |
EC2 instances can be scaled up or down based on demand |
VM Scale Sets, Autoscaling, App Service Scale Capability |
|
Instance Variety |
Broad range of EC2 instances: General Purpose, Compute Optimized, Memory Optimized, Storage Optimized, Accelerated Computing |
Wide array of VMs: General Purpose, Compute Optimized, Memory Optimized, Storage Optimized, GPU |
|
Serverless Computing |
AWS Lambda |
Azure Functions |
|
Batch Processing |
AWS Batch |
Azure Batch |
|
High-Performance Computing (HPC) |
Elastic Fabric Adapter, AWS ParallelCluster |
Azure HPC services, InfiniBand networking, CycleCloud |
|
Special ProcessorsSpecial Processors |
Graviton processors for cost-performance benefits |
N/A |
New Projects
Azure Cloud vs. AWS Cloud – Storage
A key functionality of cloud service providers is their data storage capability. Running services in the cloud involves data processing that needs to be saved at some time. AWS' storage services are the longest-running. However, Azure's storage capabilities are also highly reliable. AWS and Azure are strong in this storage category and include all the essential features, such as REST API access and server-side data encryption. Azure's storage mechanism is called Blob storage, and AWS's is called Simple Storage Service (S3).
Storage Service
AWS's cloud object storage service, Amazon S3, offers high availability and automated replication across multiple locations. Similarly, Azure Blob Storage provides robust object storage with high availability and redundancy. AWS provides block storage through Amazon EBS, which functions like hard disks and can be linked to any EC2 instance or used independently. These EBS volumes start operating when an instance begins and stop when the instance ends. In contrast, Azure uses temporary storage and page blobs for VM-based volumes, offering similar block storage capabilities through Azure Disk Storage, which provides various performance options to meet different needs.
Tired Storage Solutions
Both AWS and Azure offer tiered storage solutions to optimize costs. Amazon S3 includes S3 Standard for frequently accessed data (Hot), S3 Standard - Infrequent Access for less frequently accessed data (Cool), and Amazon Glacier for archival storage (Cold). Azure Blob Storage also provides three tiers: Hot Blob Storage for frequently accessed data, Cool Blob Storage for infrequently accessed data with additional read and write costs, and Archive Blob Storage for rarely accessed data, offering a cost-effective solution for long-term storage.
Object Size Limits
Regarding object size limits and storage capacity, AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage have robust capabilities but with some differences. AWS S3 allows each object up to 5 terabytes (TB) in size and supports multipart uploads for efficiency and reliability. On the other hand, Azure Blob Storage's Block Blobs can be up to 4.75 TB in size, Page Blobs up to 8 TB, and Append Blobs up to 4.75 TB. Despite these differences, AWS and Azure allow users to store unlimited objects, enabling businesses to scale their storage needs without worrying about hitting a limit.
|
Service |
AWS |
Azure |
|
Service Name |
S3 |
Azure Storage-Blobs |
|
Hot |
S3 Standard |
Hot Blob Storage |
|
Cool |
S3 Standard -Infrequent Access |
Cool Blob Storage |
|
Archive |
Amazon Glacier |
Archive Blob Storage |
|
Object Size Limits |
5 TB per project |
4.75 TB per Blob |
|
# of Object Limits |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Services |
AWS |
Azure |
|
Service Name |
EBS |
Managed Disks |
|
Volume Types |
Cold HDD General Purpose SSD PIOPs SSD Throughput Optimized HDD |
Standard Premium SSD |
|
Availability SLA |
99.9% |
99.9% |
|
IOPs/GB for SSD |
GP SSD -3 PIOPS SSD up to 50/GB. |
1.8 to 4.9 – This is fixed based on the disk type. |
Azure or AWS - Which is better in terms of Pricing?
Cost is a significant attraction factor for organizations planning to move to a cloud platform. With increasing competition among cloud providers, prices have continued downward for quite some time. AWS and Azure offer free introductory tiers with restricted usage limits that let users try their services before buying. Both also provide credits to grab the attention of start-ups.
-
AWS traditionally charged hourly but now offers per-second billing for many services, making it cost-efficient for short-term usage. Azure charges on a per-minute basis, but many services also use per-second billing.
-
AWS provides a pay-as-you-go model with pricing that varies based on usage: Reserved Instances for long-term commitments at discounted rates, On-Demand Instances with no upfront cost, and Spot Instances for unused capacity at reduced prices. Similarly, Azure offers pay-as-you-go pricing options for Reserved VM Instances, Spot VMs, and Azure Hybrid Benefit for cost savings using existing licenses.
|
Aspect |
AWS |
Azure |
|
Billing Criterea |
Per-second billing for some services |
Per-minute billing for most services |
|
Pricing Model |
Pay-as-you-go with various options |
Pay-as-you-go with flexible options |
|
Reserved Instances |
Available with upfront payment |
Available with upfront payment |
|
On-Demand Instances |
Pay for compute capacity by the hour |
Pay for compute capacity by the minute |
|
Spot Instances |
Bid for unused capacity at a discount |
Bid for unused capacity at a discount |
|
Hybrid Benefits |
Not applicable |
Azure Hybrid Benefit is available for BYOL and reserved VMs |
While AWS offers more flexibility and savings with increased usage, Azure also provides competitive pricing options but with slightly less flexibility in the pricing model. We recommend you visit the official pricing calculator pages– Pricing Calculator | Microsoft Azure and AWS Pricing Calculator to ensure you have the most up-to-date and accurate information about the pricing structures, options, and discounts or promotions both platforms offer.
Amazon AWS vs. Microsoft Azure – Databases
All software applications today require a database to save information. Azure and AWS provide database services, regardless of whether you need a relational database or a NoSQL offering. Amazon's RDS (Relational Database Service) and Microsoft's equivalent SQL Server database are highly available and durable and provide automatic replication.
AWS works perfectly with NoSQL and relational databases, providing a mature cloud environment for big data. AWS's core analytics offering EMR (a managed Hadoop, Spark, and Presto solution) helps set up an EC2 cluster and integrates various AWS services like Redshift and Glue, allowing you to choose the solution that best fits your needs. Azure also supports NoSQL, relational databases, and Big Data through Azure HDInsight and Azure Table. Azure provides analytical products through its exclusive Cortana Intelligence Suite, including Hadoop, Spark, Storm, and HBase. Microsoft is also increasingly promoting Azure Databricks as its premier Apache Spark analytics service.
Amazon's RDS supports six popular database engines: MariaDB, Amazon Aurora, MySQL, Microsoft SQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. Azure's SQL Database service is solely based on MS SQL Server. Azure's interface and tooling make it easy to perform various DB operations, while AWS has more instance types that you can provide to get additional control over DB instances.
Here is a fascinating insight by Tim Warner into the database services offered by both AWS and Azure, emphasizing the performance enhancements and scalability features of Amazon Aurora over traditional MySQL. In a podcast with Mike Pfeiffer, he mentioned, "So, the database engine in RDS is called Amazon Aurora, which is based on MySQL, but it's Amazon. It's their baby. They've been on it for a long time. It's basically more performance than general MySQL." On the other hand, he highlighted Azure's rich offerings, stating, "There's actually a third cloud-hosted SQL server version called Azure SQL Database Managed Instance, which is like a midway point between running SQL Server in a VM where you've got control of the virtual server and its memory allocation and SQL Engine and Azure SQL Database, which doesn't have SQL Engine." This comparison underscores the focus of both platforms on providing scalable and efficient database solutions tailored to different needs.
Azure vs AWS–Content Delivery and Networking Connectivity
A cloud service provider has several networks and collaborators that use various products to connect data centers worldwide. Users can build separate networks inside the cloud using AWS' Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Within a VPC, a user can build route tables, private IP address ranges, subnets, and network gateways. AWS also offers Direct Connect, which allows for dedicated network connections between on-premises environments and the AWS cloud, ensuring reliable and high-performance connectivity for mission-critical workloads. Similarly, Azure enables users to create private networks using Virtual Network (VNET). Azure also offers VPN Gateway and ExpressRoute for secure connectivity between on-premises data centers and Azure cloud services. AWS and Microsoft Azure provide firewall choices and solutions for extending on-premise data centers into the cloud.
The table below shows a few more parameters comparing Azure and AWS regarding content delivery and networking connectivity.
|
Service offered |
Amazon AWS |
Microsoft Azure |
|
Secluded private cloud |
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) |
Virtual Network (VNET) |
|
Content Delivery Networks Across the Globe |
CloudFront |
Azure CDN (Content Delivery Network) |
|
Management of DNS names and records |
Route 53 |
Traffic Manager Azure DNS |
|
Connection to a Dedicated Private Network |
DirectConnect |
ExpressRoute |
Amazon AWS vs. Microsoft Azure - Machine Learning
AWS and Azure provide a managed service covering the end-to-end machine learning pipeline to build, train, and deploy machine learning models faster. Although they initially had distinct features, they converged to provide similar functionalities.
Azure's ML pipeline services include Azure Machine Learning Studio, which offers a visual interface for building, training, and deploying ML models, along with Azure ML Pipelines for orchestrating complex ML workflows. On the other hand, AWS provides Amazon Sagemaker. This fully managed ML service enables data scientists and developers to build, train, and deploy ML models at scale, along with AWS Step Functions for building serverless workflows.
While Azure ML Studio initially focused on visual ML model development and SageMaker emphasized end-to-end ML lifecycle management, both platforms now offer integrated solutions covering the entire ML pipeline, including data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment. This convergence allows cloud engineers to choose between Azure and AWS based on pricing, integration with existing infrastructure, and preferred development environment.
Azure Compared to AWS: Job Opportunities
A simple keyword search on LinkedIn can quickly reveal that the jobs for AWS (300K+) are more than the jobs for Azure (200K+). The statistics suggest that AWS has better job opportunities. But don’t get carried away by the numbers because one needs to consider that AWS was launched before Microsoft’s Azure. Amazon AWS was launched in November 2004, while Azure was first introduced in October 2008. The gap in launch date means that it is highly likely that the companies dependent on AWS will be more in number. This dependency is also reflected in the companies we mentioned earlier's market share. However, it is crucial to note that both platforms are experiencing significant growth in job postings. The choice comes down to your skillset - Azure integrates well with Microsoft products, while AWS offers a broader range of services. Ultimately, gaining expertise in either cloud platform will be valuable in a future heavily reliant on cloud computing services.
Are you a beginner looking for Hadoop projects? Check out the ProjectPro repository with unique Hadoop Mini Projects with Source Code to help you grasp Hadoop basics.
AWS vs. Microsoft Azure: Salary
AWS certifications command slightly higher pay than Azure certifications. According to data from ZipRecruiter, Senior Solutions Architects in the cloud can earn an average salary of $169,455. At the same time, AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate holders can expect around $135,000 annually on average. On the Azure side, the Microsoft Certified Azure Solutions Architect Expert certification brings in an average salary of $152,000, and the Azure Administrator Associate certification offers around $125,000 annually. Reports suggest AWS certifications can yield a salary increase of 25.9%, whereas Azure certifications stand at 18.1%. While salary is a significant factor, consider other aspects like job growth, work culture, and career advancement opportunities when choosing between AWS and Azure expertise.
AWS versus Azure: Difficulty Level
Most beginners in Big Data are observed looking for an answer to the question: Which is easier to study- AWS or Azure?
An excellent answer can only come from someone with experience with both cloud platforms. Here, we are sharing the response of Arjun Bahree, a Big Data professional who has explored AWS and Azure. He suggests that AWS is pretty easy to learn compared to learning Azure. The prime reason for that is that the content of Amazon's documentation is easy to follow.
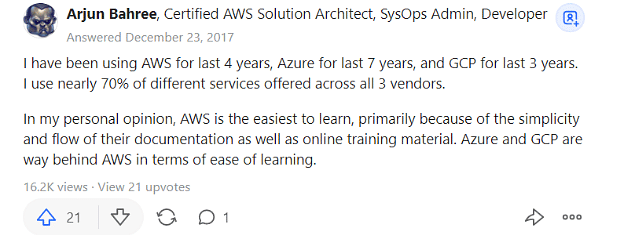
However, users comfortable with Microsoft technologies sometimes find Microsoft’s Azure easier to learn. So, depending on your needs, you can know either of them, but if you are looking for an easy cloud platform to understand without any terms and conditions, the clear answer is Amazon Web Services.
AWS vs. Azure: Market Share for Q1 2024
When aiming for job opportunities for the Big Data Cloud Engineer role, you must look at the market statistics of AWS and Azure to be more confident about your choice in learning either of them.
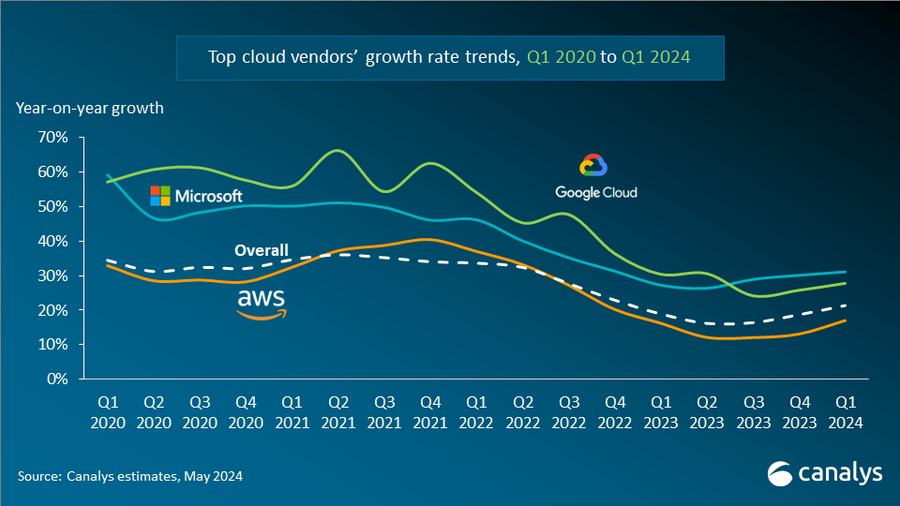
Img Source: Canalys
As per the Q1 2024 Cloud Market Share report by Canalys, global cloud infrastructure services spending surged by 21% to $79.8 billion, driven by AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. AWS maintained market leadership with 31% share and 17% growth but faced stiff competition. Microsoft Azure saw a remarkable 31% growth, fueled by AI integration and strategic partnerships like with OpenAI. Google Cloud, the third-largest provider, grew by 28%, focusing on AI advancements and global expansion. Enterprises increasingly invest in the cloud for AI integration, reshaping technology. The numbers suggest that Azure is slowly making its mark in the trading world and will continue giving stronger competition to AWS.
AWS remains the global market share leader in public cloud services at 32%, followed by Azure at 23% and Google Cloud at 10%.
Microsoft Azure versus AWS: Certifications
Certifications do not necessarily relate to capability in the broader world of work and education. But, for those of you who want to add any AWS or Azure certification to your resume, here is a list of a few certifications you might consider-
AWS Certifications
Depending on your experience level and professional area, there are presently 11 different AWS certifications you can add to your resume- a foundational certification, 3 associate-level certifications, 2 professional-level certifications, and 5 specialty certifications.
-
AWS Certified Developer- Associate
-
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator- Associate
-
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer- Professional
-
AWS Certified Solutions Architect- Professional
-
AWS Certified Advanced Networking- Specialty
-
AWS Certified Security- Specialty
-
AWS Certified Database- Specialty
-
AWS Certified Alexa Skill Builder – Specialty
Azure Certifications
Microsoft Azure certifications enhance your knowledge and skills in the current cloud technology to support the upcoming data centers, applications, and solutions.
Here is a complete list of Microsoft Azure certifications for you-
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Engineer Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
-
Microsoft Certified: Microsoft Azure IoT Developer Specialty
-
Microsoft Certified: Dynamics 365 for Sales Functional Consultant Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Dynamics 365 for Customer Service Functional Consultant Associate
-
Microsoft Certified: Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations, Functional Consultant Associate
-
Microsoft 365 Certified Fundamentals
-
Microsoft 365 Certified: Messaging Administrator Associate
-
Microsoft 365 Certified: Teamwork Administrator Associate
-
Microsoft 365 Certified: Security Administrator Associate
-
Microsoft 365 Certified: Enterprise Administrator
-
Microsoft 365 Certified: Modern Desktop Administrator
Microsoft Azure vs. Amazon AWS: Learning By Doing
You have compared AWS and Microsoft Azure services on many different technical aspects. But, the experience of using both technologies for mini Big Data projects will give you a better idea about their use cases. If you are interested in learning more about both tools by implementing projects in each, we recommend you try out these AWS and Azure projects. These project repositories have end-to-end solutions for implementing Big Data projects using the two cloud platforms. They contain beginner-friendly solution videos and downloadable source code files for your convenience. You can go through them individually and make a more calculated decision about which one you should learn: Azure or AWS.
Azure or AWS: Who will lead in the future?
Both AWS and Azure have the possibility of making a tight space for themselves in the cloud platform market as they have unique cases that hardly overlap. With its early launch, AWS was the only choice for companies seeking cloud solutions with its early launch. While the early launch gives it an edge, it initially lacked enterprise features and has only recently added them to the basket. On the other hand, Microsoft Azure possesses the capabilities to entertain enterprise clients effortlessly. It can provide the necessary support to the clients for swiftly upscaling and downscaling QA/test environments by offering economic benefits.
Azure vs. AWS - Which is better?
This article has shed some light on the AWS vs. Azure debate, but the popular question remains: Which is better: AWS or Azure? There is no clear winner in this AWS vs. Azure battle of cloud service providers, as organizations have the fortune of choosing the most attractive features from each to enable a multi-cloud strategy.
Companies that need high availability and resilience should consider multiple-data center hosting. Attempting to compare Azure and AWS is extremely difficult as both continue to launch new pricing structures, products, and integrations. However, it is important to remember that Azure is expensive but works best for companies seeking Windows integration. In contrast, if a company needs infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) or a wide range of tools, AWS would be a good option. The decision to choose either platform depends on the organization's needs and how the AWS vs. Azure comparison meets those requirements.
Regardless of the comparisons, deciding on the right public cloud service provider requires thorough research on what one needs and what the service provider has to offer. The users are likely to be the big winners in the cloud battle between AWS and Azure as each of these providers lures its customers with expanded offerings at an economical cost.
FAQs
1) Why is AWS popular than Azure?
Amazon’s AWS was launched in 2006, while Microsoft’s Azure was established in 2010. Thus, AWS has the early bird benefit and is relatively more popular than Azure. This popularity is widely reflected in its market share, which is about 13% more than that of Azure.
2) Is Azure the same as AWS?
No, Azure is a cloud platform introduced by Microsoft in 2010, whereas AWS is another cloud platform introduced by Amazon in 2006. While both platforms have similar use cases and are prevalent in the Big Data community, their parent companies are not the same.
3) Is Azure easier than AWS?
No, most people find AWS easier to use because of its easy-to-read documentation. However, depending on their preference in different use cases, Azure is sometimes people’s first choice.
4) Is AWS better than Azure?
Giving a strict yes or no answer to this question is difficult. Both cloud platforms have areas where one performs better than the other. Depending on the problem one tries to solve, the question can be answered precisely, considering all the technical aspects.
5) Is AWS bigger than Azure?
Although Azure has witnessed higher growth rates than AWS in the last four years, AWS is leading the market share with 32% as of Q1 2024.
6) How do I choose between AWS and Azure?
Compare AWS and Azure regarding storage, pricing, documentation support, and computation capabilities to analyze which will work best for your big data project.
7) What pays better, Azure or AWS?
According to a report by Burning Glass, the median salary of Azure-related jobs is $100,868, while the wages of people who possess Azure skills is $104,088. The numbers suggest that both Azure and AWS jobs pay similar salaries.
8) AWS vs Azure - Which is better for your career?
AWS has more job opportunities, which can be checked by a quick search on LinkedIn. However, it will not be appropriate today. AWS will be a better option because, as per research Burning Glass with Labour Insights, the demand for certifications and skills in Microsoft Azure is increasing. The study shows that adding those skills can produce jobs that pay you better than the market average.
9) Will Azure take over AWS?
In the first quarter of 2024, AWS has emerged as the market leader in cloud computing. However, it is interesting to note that Azure’s market share has increased in comparison to last year. Thus, there are chances that Azure will take over AWS in the near future.
About the Author
ProjectPro
ProjectPro is the only online platform designed to help professionals gain practical, hands-on experience in big data, data engineering, data science, and machine learning related technologies. Having over 270+ reusable project templates in data science and big data with step-by-step walkthroughs,



